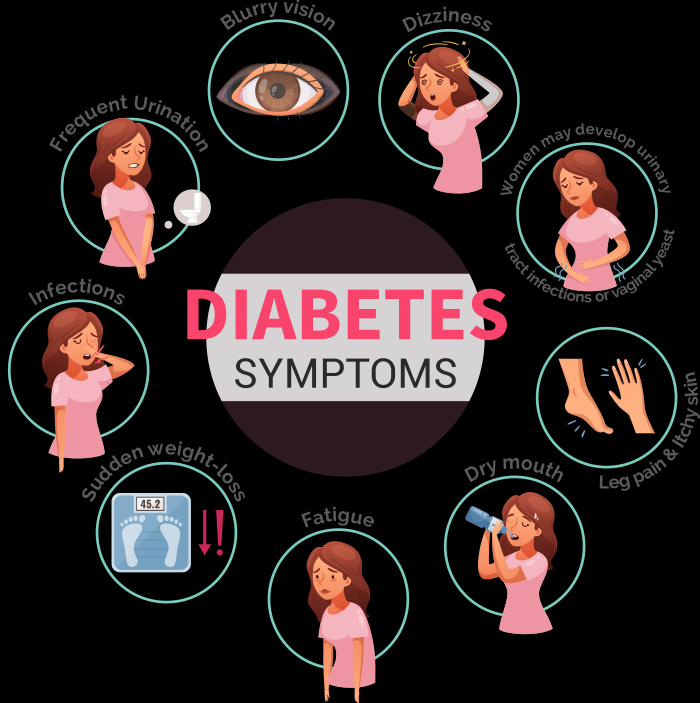
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes?
Introduction
Diabetes is a long-lasting health issue that impacts many people around the globe. It’s important to know the signs of diabetes to catch it early and handle it properly, which can help avoid serious problems. This article will walk you through the different symptoms linked to diabetes, offering a detailed overview to help you spot the signs and react accordingly.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
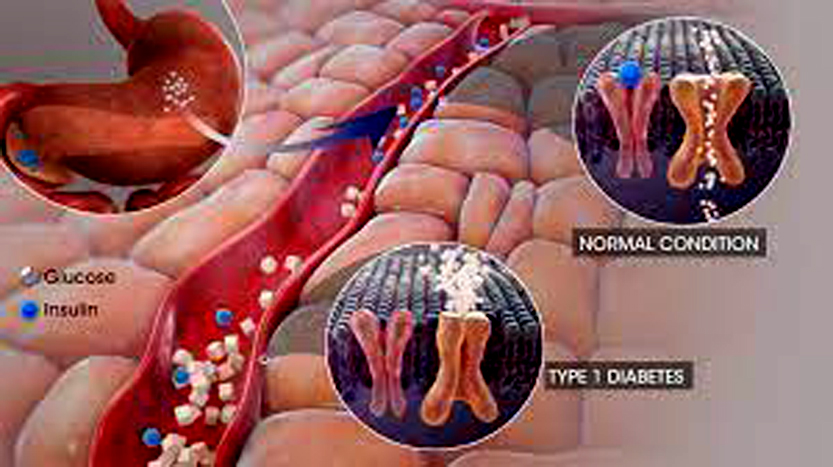
Type 1 diabetes is a lasting autoimmune issue. Here, your immune system wrongly attacks and wrecks the beta cells that make insulin in your pancreas. Insulin is crucial for letting glucose into your cells to give you energy. If you lack insulin, your blood sugar levels spike to risky heights. This kind of diabetes usually starts in kids, teenagers, and young adults, but it can happen at any age. Signs to watch for are feeling very thirsty, needing to pee often, losing weight without reason, feeling extremely hungry, being tired, and having blurry vision. Type 1 diabetes is different from type 2 because it’s not connected to how you live or what you eatManaging type 1 diabetes is a lifelong commitment that includes using insulin either through injections or a pump, monitoring your blood sugar regularly, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying active. Even though there isn’t a cure for type 1 diabetes, medical advancements and technology are making it easier for people to live healthier lives. It’s essential to detect the condition early and manage it properly to avoid complications.
Type 2 Diabetes
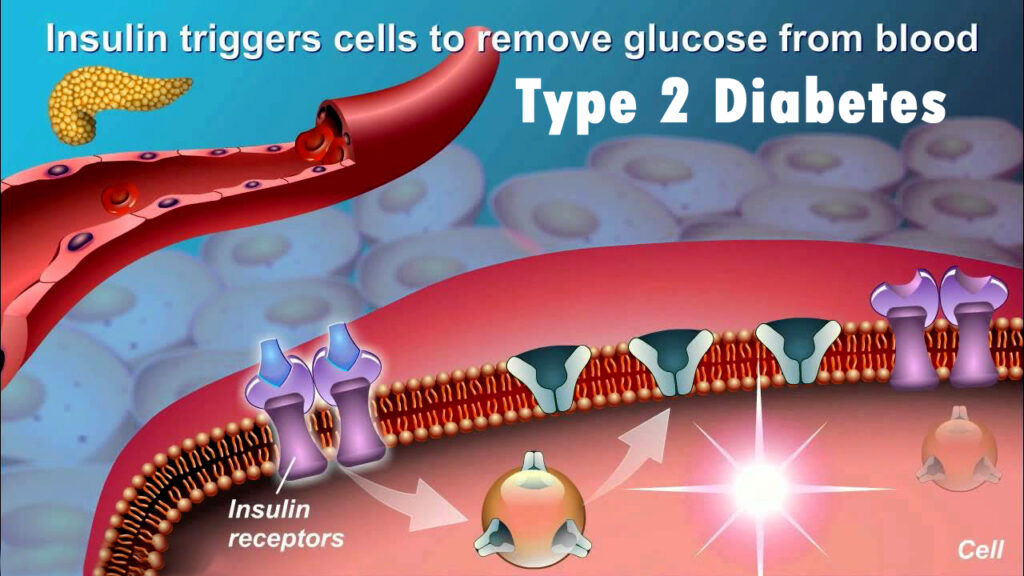
Having Type 2 diabetes means your body struggles with insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating your blood sugar levels. If not controlled, high blood sugar levels can bring about health issues. Typically, adults over 45 get diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes, yet more young individuals are affected due to higher obesity rates and inactive habits.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of type 2 diabetes like feeling thirsty all the time, needing to pee more often, increased hunger, tiredness, blurry vision, or slow-healing wounds, it’s important to pay attention. Type 2 diabetes is different from type 1 because it is often possible to control or even reverse it by making lifestyle changes. This can involve things like eating healthily, staying active, and losing weight. In some cases, medication or insulin treatment might also be needed to manage the condition effectively. It’s really important to catch health issues early and handle them well to avoid serious problems later on, such as heart disease, nerve issues, and kidney troubles.
Gestational Diabetes
When you’re pregnant, you might experience gestational diabetes. This condition typically goes away once you’ve given birth. Still, it does raise your chances of getting type 2 diabetes down the road.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination
A common sign of diabetes is feeling thirsty and needing to pee often. When your blood sugar is high, your kidneys have to work extra to remove and absorb the extra glucose, making you need to pee more often and feel thirstier.
Extreme Hunger
One more sign of diabetes is feeling very hungry. If your body doesn’t have enough insulin or if the insulin is not working well, the glucose can’t get into cells for energy, so you end up wanting more food.
Unexplained Weight Loss
If you have diabetes, you might notice that even though you’re eating more, you’re losing weight without a clear reason. This happens because your body begins to use up fat and muscle for energy when there’s not enough glucose in your cells.
Fatigue
Feeling tired and lacking energy is a typical sign of diabetes. When sugar can’t get into your cells to give you the energy you need, it makes you feel exhausted and sluggish.
Blurred Vision
When your blood sugar levels are high, it can make the lenses in your eyes swell, which can result in blurry vision. Managing your blood sugar properly can help improve this symptom.
Slow-Healing Sores and Frequent Infections
Diabetes can make it tough for your body to heal wounds and fight infections. When your blood sugar is high, it can harm your nerves and lower blood flow, which slows down the healing process.
Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet
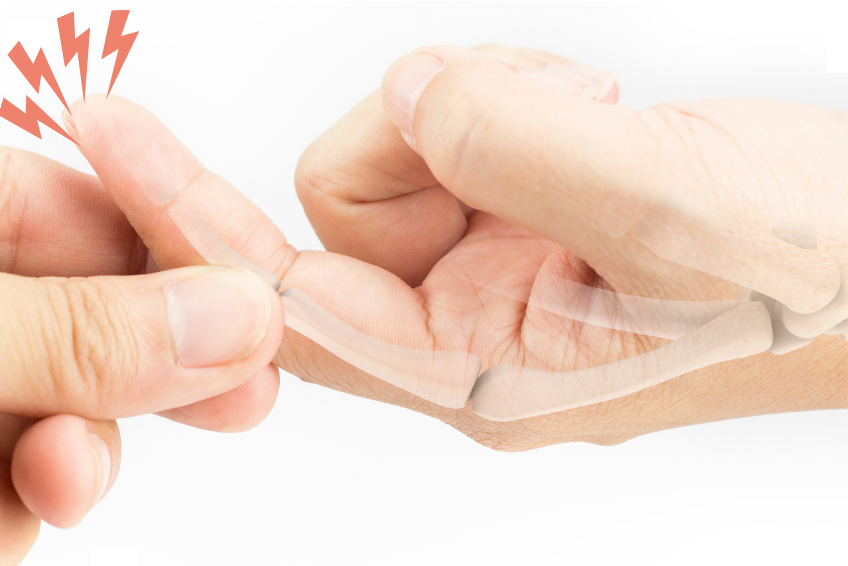

When your blood sugar levels are high, it can harm your nerves, causing a tingling or numb sensation in your hands and feet. This problem is called neuropathy and often happens to people with diabetes.
Uncommon Symptoms of Diabetes
Darkened Skin Patches
Darkened skin patches, particularly in the armpits and neck, can be a sign of insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Gum Disease and Mouth Problems
Having diabetes can up your chances of developing gum disease and other oral issues. When your blood sugar is high, it can cause more glucose in your saliva, which can encourage the growth of bacteria and lead to gum infections.
Irritability and Mood Changes
Fluctuations in your blood sugar levels can impact how you feel and may cause irritability and shifts in your mood. Keeping your blood sugar in check can assist in balancing out these mood changes.
Persistent Itching
Continual itching might indicate diabetes. When your blood sugar is high, it can result in dry skin and reduced blood flow, which can cause itching and various skin issues.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
If diabetes runs in your family, you are more likely to develop it. Genes have a big impact on getting type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Factors
An unhealthy diet, not moving much, and being overweight are big reasons why people get type 2 diabetes. If you don’t get up and move around enough, your body might not respond well to insulin, and your blood sugar could go up.
Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hypertension can raise the chances of getting diabetes.
Diagnosis and Tests
Blood Tests
You can find out if you have diabetes through various blood tests. These tests include checking your fasting blood sugar, doing an A1C test, and undergoing an oral glucose tolerance test.
Urine Tests

When you take a urine test, it can show if you have too much glucose and ketones in your body. This could mean you’re not managing your blood sugar well and might have diabetes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Urine tests are able to show if there are high amounts of glucose and ketones, which could mean that your blood sugar is not well managed and that you might have diabetes.
Treatment Options
Medications
Several medications can help manage diabetes, including insulin, metformin, and other oral or injectable drugs.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management, are crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications.
Alternative Therapies
When it comes to dealing with diabetes symptoms, options like acupuncture and specific dietary supplements could be beneficial. Nonetheless, before exploring these alternative therapies, make sure to talk to a healthcare professional first.
Preventive Measures
Healthy Diet

A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect diabetes early and manage the condition effectively.
Personal Stories
Sharing personal stories of individuals living with diabetes can provide valuable insights and encouragement to others facing similar challenges.
Expert Insights
Expert insights from medical professionals can offer guidance on managing diabetes and staying healthy.
Conclusion
Knowing the signs of diabetes is crucial for catching it early and controlling it well. By spotting the symptoms and adapting your lifestyle, you can live a healthy and satisfying life even with diabetes. Keep yourself educated, take charge of your health, and make sure to see your healthcare provider regularly to handle your diabetes properly.